All content on this website is for informational purposes only, and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. If you have questions about your medical condition or treatment, always seek advice of your physician or other qualified healthcare professional.
Hypertension
High blood pressure, also called hypertension, is a condition characterised by elevated pressure within the blood vessels. Higher pressure requires greater effort from the heart to pump blood effectively and poses a significant risk of various health complications, including heart disease, heart attack, and stroke.
Having blood pressure numbers consistently above normal may result in a diagnosis of hypertension.
Healthcare professional can diagnose hypertension and make treatment decisions by examining the systolic and diastolic blood pressure levels and comparing them with the levels indicated in official guidelines.
0/4
men having the condition (1)
0/5
women having the condition (1)
Blood pressure arises from the force exerted by blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels (arteries).
Your blood pressure normally rises and falls throughout the day.
Blood pressure is measured using two numbers (2):
- The first number, called systolic blood pressure, measures the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats.
- The second number, called diastolic blood pressure, measures the pressure in your arteries when your heart rests between beats.
If the measurement reads 117 systolic and 78 diastolic, you would say, “117 over 78,” or write, “117/78 mmHg (millimeters of mercury).”
A normal blood pressure for an adult, is usually less than 120/80 mmHg. Please talk to your doctor or healthcare professional.
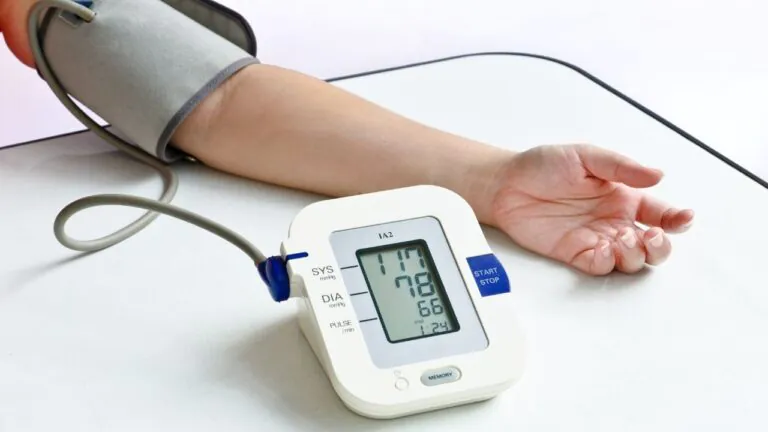
High blood pressure usually has no warning signs or symptoms, and many people do not know they have it. Measuring your blood pressure is the only way to know whether you have high blood pressure (2).
0 billion
adults aged 30–79 years worldwide have hypertension (3)
0%
of adults with hypertension are unaware they have the condition (3)
High blood pressure can damage your health and seriously hurts important organs like the heart, brain, kidneys and eyes (2).
Poorly controlled hypertension puts you at increased risk for cardiac disease (congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, angina, left ventricular hypertrophy, and arrhythmias), cerebrovascular disease (stroke and cognitive decline), renal disease (chronic renal failure and dialysis), and vascular disease (accelerated atherosclerosis and retinopathy) (4)
It is important to detect hypertension as early as possible so the respective treatment can begin. If you have concerns about your risk or blood pressure numbers, talk to your doctor or healthcare provider.
0%
of people with hypertension have been diagnosed (4)
0%
of adults with hypertension are diagnosed and treated (3)
0%
of people with hypertension have controlled blood pressure (4)
How to prevent health burden?
The greatest gift you can give yourself and your loved ones is a healthy you. Take care of your body and focus on living the highest quality of life you can through your daily choices.
At Acino, we have longstanding knowledge which we want to share with you. Explore our materials to raise your awareness, and make decisions to stay healthy and improve your quality of life.
Know what causes high blood pressure? (2,3)
- genetics
- older age – high blood pressure usually develops over time
- certain health conditions such as diabetes and having obesity
- unhealthy lifestyle – not enough physical activity, high-salt diet, drinking too much alcohol, etc.
How to keep your blood pressure at a healthy range? (6)
Some factors are uncontrollable, such as age, family history, race or ethnicity. But you can take steps to lower the risks you can control:
- Eat and drink healthy: The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) eating plan has proven record of helping people lower their blood pressure.
- Choose foods that are low in sodium — an element in table salt often present in processed and restaurant foods — and rich in potassium — a mineral that your body needs to work properly. Potassium is found in many foods; bananas, potatoes, beans, and yogurt have high levels of potassium.
- Determine whether your weight is in a healthy range, doctors often calculate your body mass index (BMI).
- Limit alcohol consumption.
- Be physically active:
- Take the stairs instead of the lift.
- Walk or use a bicycle even for short distances.
- Incorporate physical activity into a daily routine.
- Quit or never start smoking. All types of smoking and passive smoking increase the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
- Get enough sleep
Measure your blood pressure regularly to detect any health problems early.
You can get your blood pressure checked (5):
- By a healthcare professional at a doctor’s office.
- At a pharmacy that has a digital blood pressure measurement machine.
- With a home blood pressure monitor that you can use yourself.
However, be aware that many things can affect a blood pressure reading, including nervousness, what you ate, drank or did before your reading, and even how you are sitting. It is therefore important to get an accurate blood pressure reading so that you have a clearer picture of your risk.
Acino has prepared a printable leaflet for you, which will help you:
- Learn the correct way to measure blood pressure
- Prepare you first blood pressure visit
- Keep track of your blood pressure checks at home
Download Acino Leaflet – Manage Blood Pressure
Take your medicine (6).
Talk with your doctor or healthcare professional about the best type of treatment for you. You may need to take more than one type of medicine to control your blood pressure. Blood pressure medicines can work several different ways. Blood pressure medicines can keep blood pressure at a healthy level by:
- Causing your body to get rid of water, which decreases the amount of water and salt in your body to a healthy level
- Relaxing your blood vessels
- Making your heartbeat with less force
- Blocking nerve activity that can restrict your blood vessels
If you take medicine to treat high blood pressure or other health conditions, follow your doctor’s or healthcare professional’s instructions carefully.
One of the global targets for non-communicable diseases is to reduce the prevalence of hypertension by 33% between 2010 and 2030 (3).
Download our educational poster*, and spread the word:
Join us on Facebook and let’s talk hypertension disease, especially during the World Hypertension Day on 17 May every year.
Last update: 5 April 2024
(GLO-CV-Apr-2024-003)
References
1. World Health Organization, Hypertension. Accessed 20 March 2024
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, High Blood Pressure Symptoms and Causes. Accessed 20 March 2024
3. World Health Organization, Hypertension – Fact Sheets. Accessed 20 March 2024
4. Edwards EW, Saari HD, DiPette DJ. Inadequate hypertension control rates: A global concern for countries of all income levels. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2022 Mar;24(3):362-364. doi: 10.1111/jch.14444. Epub 2022 Feb 24. PMID: 35199940; PMCID: PMC8924991.
5. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Measure Your Blood Pressure. Accessed 20 March 2024
6. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Prevent and manage High Blood Pressure. Accessed: 20 March 2024
* Downloadable materials
This material is intended solely for the general information. It is not to be used for treatment or diagnostic purposes, but rather for discussion with the patient’s own physician. The information contained herein is neither intended to dictate what constitutes reasonable, appropriate or best care for any given health issue, nor is it intended to be used as a substitute for the independent judgment of a physician for any given health issue.